Transcription of THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK • THE STATE ...
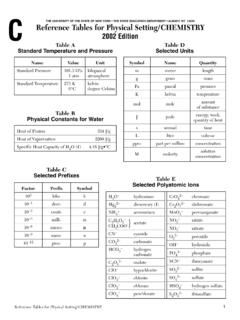
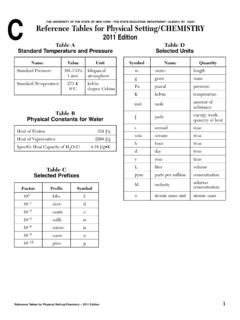
1 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY 12234 reference Tables for Physical Setting/ PHYSICS2006 EditionList of Physical ConstantsNameSymbolValueUniversal gravitational 10 11 N m2/kg2 Acceleration due to m/s2 Speed of light in a 108m/sSpeed of sound in air at 102m/sMass of 1024 kgMass of the Moon 1022 kgMean radius of 106mMean radius of the 106mMean distance Earth to the 108mMean distance Earth to the 1011mElectrostatic 109N m2/C21 elementary 10 19C1 coulomb (C) 1018elementary charges1 electronvolt (eV) 10 19 JPlanck s 10 34J s1 universal mass unit (u) 102 MeVRest mass of the 10 31kgRest mass of the 10 27kgRest mass of the 10 27kgPrefixes for Powers of 10 PrefixSymbolNotationteraT1012gigaG109meg aM106kilok103decid10 1centic10 2millim10 3micro 10 6nanon10 9picop10 12 Approximate Coefficients of FrictionKineticStaticRubber on concrete (dry) on concrete (wet) on asphalt (dry) on asphalt (wet) on ice ski on on on on on Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 EditionPage 2102110201019101810171016101510141013101 210111010109108107106105 Gamma RaysX raysUltravioletInfraredMicrowavesTV,FMAM R adio WavesLong Radio WavesVisible Light(not to scale)
2 VioletBlueGreen Yellow 1014 Wavelength in a vacuum (m)Frequency (Hz)10 1310 1210 1110 1010 910 810 710 610 510 410 310 210 1100101102103104 The Electromagnetic SpectrumAbsolute Indices of Refraction(f= 1014Hz) , , , Level DiagramsClassification of MatterParticles of the Standard ModelHydrogenEnergy Levels for the Hydrogen AtomGround StateIonization 1n= 2n= 3n= 4n= 5n= 6n= (eV)AFew Energy Levels for the Mercury AtomMercuryGround StateIonization (eV)hi tCharge+ e+e+edownstrangebottomds b e e eLeptonselectronmuontaue 1e 1e 1eelectronmuontauneutrinoneutrinoneutrin o e 00 0 Note:For each particle, there is a corresponding antiparticle with acharge opposite that of its associated andquarksantiquarkReference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 EditionPage 3 reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 EditionPage 4 Resistivities at 20 CMaterialResistivity ( m) 10 10 10 8 Nichrome150.
3 10 10 10 8 Circuit Symbolscellbatteryswitchvoltmeterammeter resistorvariable resistorlampSeries CircuitsI= I1 = I2= I3= ..V= V1+ V2+ V3+ ..Req= R1+ R2+ R3+ ..Parallel CircuitsI= I1+ I2+ I3+ ..V= V1= V2= V3= ..= + + + ..1R31R21R11 ReqElectricityA= cross-sectional areaE= electric field strengthFe= electrostatic forceI= currentk= electrostatic constantL= length of conductorP= electrical powerq= chargeR= resistanceReq= equivalent resistancer = distance between centerst= timeV= potential differenceW= work (electrical energy) = change = resistivityFe= E= V= I= R= R= P= VI = I2R = W= Pt= VIt= I2Rt= V2tRV2R LAVI qtWqFeqkq1q2r2 VAReference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 EditionPage 5 Wavesv= f T= i= rn= n1sin 1= n2sin 2= = Modern PhysicsEphoton=hf =Ephoton= Ei EfE = mc2 Geometry and TrigonometryRectangleA = bhTriangleA= bhCircleA= r2C= 2 rRight Trianglec2= a2+ b2sin = cos = tan = abbcac12hc 1 2v1v2n2n1cv1fc= speed of light in a vacuumf = frequencyn= absolute index of refractionT= periodv= velocity or speed = wavelength = angle i= angle of incidence r= angle of reflection c= speed of light in a vacuumE= energy f = frequencyh= Planck s constantm= mass = wavelengthA= areab=
4 BaseC= circumferenceh= heightr= radius abc90 reference Tables for Physical Setting/Physics 2006 EditionPage 6= a= vf= vi+ atd= vit+ at2vf2= vi2+ 2adAy= Asin Ax= Acos a= Ff= FNFg= g= p= mvpbefore= pafterJ= Fnett= pFs= kxPEs= kx2Fc= macac= PE= mg hKE= mv2W= Fd= ETET= PE+ KE+ QP= = = Fa= accelerationac= centripetal accelerationA= any vector quantityd= displacement or distanceET= total energyF= forceFc= centripetal forceFf = force of frictionFg= weight or force due to gravityFN= normal forceFnet= net forceFs= force on a springg= acceleration due to gravity orgravitational field strengthG= universal gravitational constanth= heightJ= impulsek= spring constantKE= kinetic energym= massp= momentumP= powerPE= potential energyPEs= potential energy stored in a springQ= internal energyr= radius or distance between centerst= time intervalv= velocity or speed= average velocity or average speedW= workx= change in spring length from the equilibrium position = change = angle = coefficient of frictionvvFdtWt12v2r12 FgmGm1m2r2 Fnetm12 vtdtvDET 615 96-05540 96-040 CDCM echanics