Search results with tag "Electrophilic"
Reactions of Benzene & Its Derivatives
colapret.cm.utexas.eduElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution • Electrophilic aromatic substitution: a Electrophilic aromatic substitution: reaction in which a hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced by an electrophile • In this section: – several common types of electrophiles – how each is generated – the mechanism by which each replaces hydrogen + + H ...
Benzene and Its Derivatives
pa01000125.schoolwires.net9.5 What Is Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution? 9.6 What Is the Mechanism of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution? 9.7 How Do Existing Substituents on Benzene Affect Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution? 9.8 What Are Phenols? HOW TO 9.1 How to Determine Whether a Lone Pair of Electrons Is or Is Not Part of an Aromatic Pi System
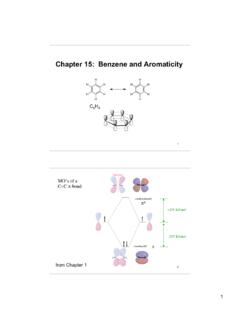
Chapter 15: Benzene and Aromaticity - College of Arts and ...
as.vanderbilt.eduThe π-bonds of benzene are resistant to the normal reactions of alkenes and alkynes Br Br Cl CHO CHO Br 2 HCl O 3 No Reaction Benzene’s cyclic conjugated structure gives it special stability 12 Benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions (chapter 16) rather than electrophilic addition +BrBr Br Br Br +HBr Fe catalyst electrophilic ...
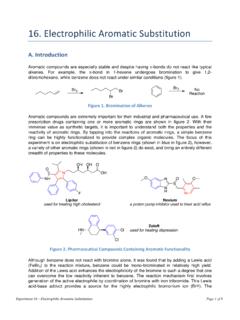
16. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
community.wvu.eduExperiment 16 – Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Page 5 of 8 acetanilide under electrophilic nitration conditions to determine experimentally which of the two substrates is more reactive. (Figure 9) Figure 9. Nitration of an Aromatic Ring Ortho/Para Selectivity with an Activating Group
AMIDES AND RELATED FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
webhome.auburn.edureactions: The relatively low electrophilicity of amide carbonyl groups is reflected by their resistance to hydrolysis relative to functional groups such as esters. Recall that the presence of a carbonyl (C=O) and ether (O-C) dipole renders the "central" carbonyl carbon of an ester electron deficient; it is an electrophilic carbon atom.
Professor J. Stephen Clark
www.chem.gla.ac.uk• Electrophilic substitution reactions of pyrroles, furans and thiophenes • Metallation of five-membered heteroaromatics and use the of directing groups • Strategies for accomplishing regiocontrol during electrophilic substitution Indoles • Comparison of electronic structure …
Carbonyl Chemistry – Fundamentals - UCLA
www.chem.ucla.edu- Attack on a carbonyl could create a new stereocenter4 2. Electrophilic attack at _- oxygen - lone pairs & pi bond help electrophilic attack - requires strong acid (H
Organi II Mechanisms - Organic chemistry
www.slooporganicchemistry.comd. Electrophilic aromatic substitution (Alkylation): e. Electrophilic aromatic substitution (Acylation): f. Nucleophilic substitution reaction of aryl halides with EWG (Meisenheimer complex;
Organic Reactions andOrganic Reactions and Their ...
polymer.zju.edu.cnIn a substitution reaction, a functional group in a particular chemical compound is replaced by another group. Reagent Substrate Reactive intermediate Type of organic substitution Nucleophilic Aliphatic Carbocation Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution Electrophilic Aromatic Carbanion Aromatic electrophilic substitution Free radical substitution
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - chez-alice.fr
jsforum.chez-alice.frElectrophilic Carbon / 220 Reactivity Matching / 223 Generation of Nucleophilic Carbon Reagents / 224 Generation of Electrophilic Carbon Reagents / 227 Matching Nucleophiles with Electrophiles / 227 Enolates / 228 Enolate Regioisomers / 234 Diastereoselection in Aldol Reactions / 236 Organometallic Compounds / 239 Neutral Carbon Nucleophiles / 239
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds - Rutgers University
crab.rutgers.eduWhen a reaction proceeds this way, it is electrophilic aromatic substitution. There are a wide variety of electrophiles that can be introduced into a benzene ring in this way, and so electrophilic aromatic substitution is a very important method for the synthesis of substituted aromatic compounds.
Nitration of Toluene (Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution)
www.cerritos.edubenzene in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Toluene undergoes nitration to give ortho and para nitrotoluene isomers, but if heated it can give dinitrotoluene and ultimately the explosive trinitrotoluene (TNT). Figure 2: Reaction of …
Reaction Mechanisms - IITPK
www.iitpk.comElectrophilic substitution (SE2) is every common in benzene nucleus (aromatic compounds) in which . π electrons are highly delocalized and an electrophile can attack the region of high electron density. Aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions involve the following 3 steps mechanism : Step-1: The formation of an electrophile. Step-2
Unit 10 - NCERT
ncert.nic.in(i) From hydrocarbons by electrophilic substitution Aryl chlorides and bromides can be easily prepared by electrophilic substitution of arenes with chlorine and bromine respectively in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts like iron or iron(III) chloride. The ortho and para isomers can be easily separated due to large,
Professor J. Stephen Clark
www.chem.gla.ac.ukPyridines – Electrophilic Reactions N αααα ββββ γγγγ N E N E E N E E E E −E Pathways for the Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of Pyridines • The position of the equilibrium between the pyridine and pyridinium salt depends on the substitution pattern and nature of the substituents, but usually favours the salt
ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY - University of Nairobi …
profiles.uonbi.ac.kepathway require a strong nucleophile attacking an electrophilic site to be effective. Such reactions are of limited scope. For instance, the formation of biaryl systems via the classical substitution reaction is difficult to achieve. 12:44 PM
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds - Rutgers University
crab.rutgers.edutoward electrophilic aromatic substitution, and that the methyl group is an activating group). 2) Nitration of toluene generates a mixture of products. The major products are those with substitution at the ortho and para positions. (This preference for o/p substitution makes the methyl group an ortho/para director).
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic …
www.utdallas.eduElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution! Aromatic compounds react through a unique substitution type reaction! Initially an electrophile reacts with the aromatic compound to generate an arenium ion!
HHALAL ARENEARENESS …
ncert.nic.in44. Aryl chlorides and bromides can be easily prepared by electrophilic substitution of arenes with chlorine and bromine respectively in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts. But why does preparation of aryl iodides requires presence of an oxidising agent? 45. Out of o-and p-dibromobenzene which one has higher melting point and why? 46.
A NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTION
www.people.vcu.edunucleophilic substitution. The nucleophile, or electron rich species, attacks the electrophilic carbon of the alkyl group to give the substituted product. A different nucleophile is generated as a by-product of the reaction. Table E26-1 on the following page gives a number of examples of nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Cambridge International AS & A Level
www.cambridgeinternational.org4 (a)4-nitromethylbenzene can be prepared via an electrophilic substitution reaction as shown in Fig. 4.1. CH 3 conc. HNO 3 conc. H 2 SO 4 methylbenzene CH 3 H NO 2 intermediate T CH 3 NO 2 4-nitromethylbenzene Fig. 4.1 (i)This reaction also forms an isomer of 4-nitromethylbenzene as a by-product. Draw the structure of this by-product. [1]
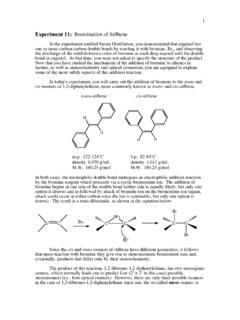
Experiment 11: Bromination of Stilbene
www.bc.eduIn both cases, the nucleophilic double bond undergoes an electrophilic addition reaction by the bromine reagent which proceeds via a cyclic bromonium ion. The addition of bromine begins at one side of the double bond (either side is equally likely, but only one option is drawn) and is followed by attack of bromide ion on the bromonium ion (again,
SYLLABUS FOR M.Sc CHEMISTRY - Andhra University
andhrauniversity.edu.inII SEMESTER Course/Paper - III: Organic Chemistry - 2 , UNIT - I Aromatic substitution reactions - electrophilic, nucleophilic and through benzynes - radical
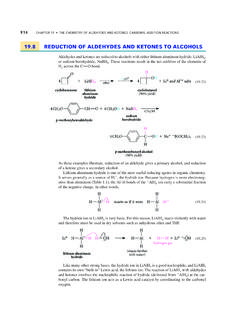
19.8 REDUCTION OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES TO …
www.saplinglearning.commakes the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic (that is, makes it more reactive toward nucle-ophiles) by making the carbonyl oxygen a better acceptor of electrons. The carbon group of the Grignard reagent reacts as a nucleophile at the carbonyl carbon. Recall that this group is a strong base that behaves much like a carbanion (Secs. 8.8B and 11.4C).
10 Reactions of Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides, Amines, and
www.pearsonhighered.comundergo a subsequent electrophilic addition reaction with HBr to form more of the substitution product (Section 6.1). Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution reactions with hydrogen halides faster than secondary alcohols do because tertiary carbocations are more stable and, therefore, are formed more rapidly than secondary carbocations.
Organometallic Compounds - IIT Kanpur
home.iitk.ac.inElectrophilic: Such molecules do contain electro-negative atoms and are good oxidizing agents. They are often considered to be “reactive” substrates. These molecules do not require the presence of an empty orbital (18e-is OK) on the metal center in order to perform the oxidative addition reaction. Examples: X 2 (X = Cl, Br, I), R-X, Ar-X, H ...
Chemical Tests for Alkanes, Alkenes, and Aromatic Compounds
www.physci.mc.maricopa.eduAromatics also undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Although aromatics are highly unsaturated, they do not participate in addition reactions like the alkenes, since the loss of double bonds would lead to a loss of resonance and aromatic character. These aromatic substitution reactions generally occur in the presence of
HYDROCARBONS 365 - NCERT
www.ncert.nic.inof electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene; • predict the directive influence of substituents in monosubstituted benzene ring; • learn about carcinogenicity and toxicity. HYDROCARBONS The term ‘hydrocarbon’ is self-explanatory which means compounds of carbon and hydrogen only. Hydrocarbons play a key role in our daily life.
Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
as.vanderbilt.eduChapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions As a result of the large dipole of the carbonyl group: 1. The carbonyl carbon is electrophilic and is the site of addition reactions by nucleophiles; 2. The α-protons are acidic and can be deprotonated by strong bases to give an enolate, which are nucleophiles and react with electrophiles. C CH O B ...
Carboxylic Acids - Rutgers University
crab.rutgers.eduelectrophilic. Therefore acid chlorides are very reactive with nucleophiles, usually through the nucleophilic acyl substitution mechanism. The best way to make acid chlorides is the reaction of a carboxylic acid with either thionyl chloride (SOCl …
Genetics and Genomics Chapter 4 Questions & Answers ...
online.universita.zanichelli.itd) electrophilic alkylating agents e) automobile fumes i) intrastrand base cross-linking ii) interstrand base cross-linking iii) aromatic hydrocarbon DNA adducts iv) increased reactive oxygen species (ROS)- mediated damage Answer 4.3 a) iv) b) iii) c) i) d) ii) e) iii) Explanation 4.3
Reactions of Alkenes
www.vanderbilt.eduReactions of Alkenes Product Type of Reaction (name) Reaction Conditions Regiochemistry Stereochemistry Halides (Ch 6.9) Electrophilic Addition HX, organic solvent (anhydrous) Markovnikov Addition No stereochemical pref. (Ch. 7.10) Radical Chain HBr, H2O2, hν Anti-Markovnikov No stereochemical pref.
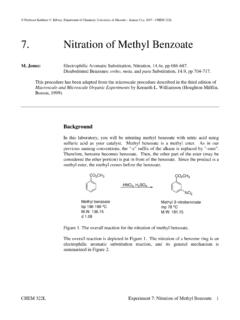
7. Nitration of Methyl Benzoate - UMKC
d.web.umkc.eduM. Jones: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution, Nitration, 14.4e, pp 686-687. Disubstituted Benzenes: ortho, meta, and para Substitution, 14.9, pp 704-717. This procedure has been adapted from the microscale procedure described in the third edition of Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments by Kenneth L. Williamson (Houghton Mifflin ...
B.Sc. - FIRST YEAR
mjpru.ac.inAromatic electrophilic substitution – general pattern of the mechanism, role of σ and π complexes, Mechanism of nitration, halogenation, sulphonation, mercuration and Friedel-Crafts reaction. Energy profile diagrams. Activating and deactivating substituents, orientation and ortho/para ratio, Side chain ...
1) Stability of Carbocations - Rutgers University
crab.rutgers.edu1 This big chapter will cover: 1) Stability of Carbocations 2) Formation of Carbocations (a) ionization (b) addition to a πbond (c) Alkyl Halide and a Lewis Acid 3) The Fate of Carbocations 4) Rearrangements of Carbocations 5) Electrophilic Addition (a) Regiospecificity (b) Stereochemistry 6) Acid catalyzed Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds (a) Hydrolysis of …
Aromatic Compounds
www.crab.rutgers.eduCh16 Aromatic Compounds (landscape).docx Page 1 Aromatic Compounds ... and undergo electrophilic additions with halogens (Br 2). ... cyclo-alkenes. Ch16 Aromatic Compounds (landscape).docx Page 5 When a catalyst is added to the benzene bromination reaction, reaction does occur, but the reaction is not an addition, but rather a substitution ...
Reactions of Fats and Fatty Acids
butane.chem.uiuc.eduelectron poor and so an electrophilic center. The oxygen if methanol has 2 lone pairs of electrons, making it a nucleophile. Before nucleophilic substitution can take place, the alkoxide oxygen on the ester must be protonated to make it a better leaving group.
Unit - NCERT
www.ncert.nic.inunsymmetrical alkenes, the addition reaction takes place in accordance with Markovnikov’s rule (Unit 13, Class XI). Mechanism The mechanism of the reaction involves the following three steps: Step 1: Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by electrophilic attack of H3O +. H2O + H + +→ H 3O Step 2: Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS …
www.saplinglearning.com16.5 ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS OF SUBSTITUTED BENZENES 763 nal substituent group is called a meta-directing group. Thus, the nitro group is a meta-directing group because all electrophilic substitution reactions of nitrobenzene occur at the
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions - UCLA
www.chem.ucla.eduElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions, Course Notes Archive, 4 Disclaimer: All images are borrowed from: Bruice, P. Organic Chemistry.Pearsons Prentice Hall, 2004.
ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS …
www.saplinglearning.com16.4 ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS OF BENZENE 755 Step 2 Reaction of the benzene p electrons with the electrophile to form a carbocation inter- mediate. (Notice that either of the oxygens can accept the electron pair.) Step 3 Loss of a proton from the carbocation to give a new aromatic compound. Nitration is the usual way that nitro groups are …
ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS OF …
www.saplinglearning.com16.4 ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS OF BENZENE 755 Step 2 Reaction of the benzene p electrons with the electrophile to form a carbocation inter- mediate. (Notice that either of the oxygens can accept the electron pair.) Step 3 Loss of a proton from the carbocation to give a new aromatic compound. Nitration is the usual way that nitro groups are introduced into aromatic rings.
Similar queries
ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION, Aromatic, Reactions, Electrophilic, AMIDES, Amide, Organi II Mechanisms, Substitution, Substitution Electrophilic Aromatic, Aromatic electrophilic substitution, ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, Reaction, Substitution reactions, Electrophilic substitution, Aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions, ORGANOMETALLIC, Reactions of Aromatic Compounds, Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic, Electrophilic Aromatic, Experiment 11: Bromination of Stilbene, SYLLABUS, Aromatic substitution reactions, 19.8 REDUCTION OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES TO, HYDROCARBONS 365, Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions, 7. Nitration of Methyl Benzoate, 1) Stability of Carbocations, Fatty Acids, ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS, ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS OF