Search results with tag "Sapling learning"
9.6 THE SN1 AND E1 REACTIONS - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com414 CHAPTER 9 • THE CHEMISTRY OF ALKYL HALIDES The base that removes a b-proton from the carbocation is typically a solvent molecule. Although ethanol is a very weak base, the reaction occurs readily because ethanol, as the sol-
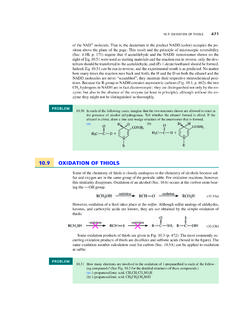
10.9 OXIDATION OF THIOLS - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com10.9 OXIDATION OF THIOLS 471 of the NAD| molecule. That is, the deuterium in the product NADD (color) occupies the po-sition above the plane of the page. This …
7.4 DISUBSTITUTED CYCLOHEXANES - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com282 CHAPTER 7 • CYCLIC COMPOUNDS. STEREOCHEMISTRY OF REACTIONS In a different stereoisomer of 1-chloro-2-methylcyclohexane, the chloro and methyl groups occupy adjacent equatorial and axial positions.
STUDY GUIDE LINK 7 - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com7.9 STEREOCHEMISTRY OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS 305 The trans diastereomer can exist as a pair of enantiomers, and the two enantiomers of the cis di-astereomer are rapidly equilibrated by the chair interconversion and cannot be separated (Sec.
11.2 SYNTHESIS OF EPOXIDES - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com11.2 SYNTHESIS OF EPOXIDES 489 To understand why epoxidation occurs so readily, we’ll take the same approach that we used in Chapter 5 to …
6 Principles of Stereochemistry - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com228 CHAPTER 6 • PRINCIPLES OF STEREOCHEMISTRY hands—the relationship of an object and its noncongruent mirror image. Thus, 2-butanol is a chiral molecule. Molecules (or other objects) that are not chiral are said to be achiral—with-
3.4 BRØNSTED–LOWRY ACIDS AND BASES - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com96 CHAPTER 3 • ACIDS AND BASES. THE CURVED-ARROW NOTATION 3.4 BRØNSTED–LOWRY ACIDS AND BASES A. Definition of Brønsted Acids and Bases Although less general than the Lewis concept, the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base concept pro- vides another way of thinking about acids and bases that is extremely important and useful in
8.4 SOLVENTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Sapling Learning
www.saplinglearning.com8.4 SOLVENTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 339 8.14 Label each of the following molecules as a hydrogen-bond acceptor, donor, or both. Indicate the hydrogen that is donated or the atom that serves as the hydrogen-bond acceptor.