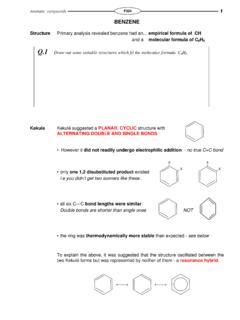
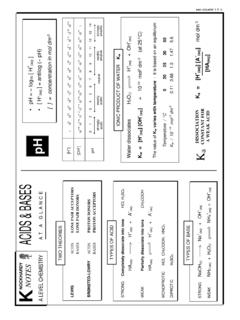
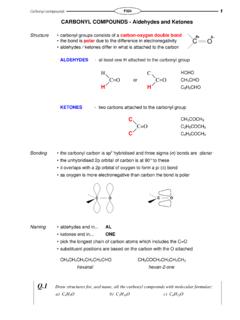
Transcription of STEREOISOMERISM - knockhardy.org.uk
1 KNOCKHARDY NOTESA LEVEL CHEMISTRYISOMERISMAT A GLANCE J. L. HOPTON 1999 ISOMERISMSTEREOISOMERSSTRUCTURAL ISOMERSGEOMETRICAL ISOMERSOPTICAL ISOMERSSame molecular formula - different structural formulaGroups fixed in different space asa result of the restricted rotationof double bonds fixed in different space as aresult of the asymmetry of the mirror images of each structural formula, differentarrangement of groups in ISOMERISMcan occur due to variations in .. the carbon skeletonbutane and 2-methylpropane positions of a functional1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane group on a chain but-1-ene and but-2-ene functional groupacids and estersalcohols and ethers3CH22 CHCH3 CHCH33 CHCH3 CHCH3 CCHHH2 CHCCCH3CH3 HHCH3CH2CH2Cl CH3 CHClCH3 OHHHCHCHHHHCHOCHHHSTEREOISOMERISMGEOMETR ICAL isomerism a form of STEREOISOMERISM found in alkenes occurs due to the restricted rotation of C=C double bonds doesn t occur with single bonds because they can rotate the two forms are known as CIS and TRANS doesn t occur when two similar groups / atoms are on the
2 Same endof the double bondCCCH3CH3 HHCCCH3CH3 HHCISTRANSOPTICAL isomerism a form of STEREOISOMERISM the different forms are known as optical isomers or enantiomers occurs when compounds have an asymmetric carbon atom occurs when compounds have 4 different groups attached to the same carbon TWO isomers which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other isomers differ in their reaction to plane-polarised light one isomer rotates light to the right - DEXTROROTATORY the other rotates light to the left - LAEVOROTATORY rotation of light is measured using a polarimeter rotation is measured by observing the polarised light coming towards the observer an 50-50 mixture of the two enantiomers is a racemic mixtureCOH3 CHH5C2 BrAACCDDBB