Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
23.1 Mechanism of Carbonyl Condensation Reactions An enolate of one carbonyl (nucleophile) reacts with the carbonyl carbon (electrophile) of a second carbonyl compound (1,2-addition reaction) resulting in the formation of a new C-C bond General mechanism (Fig. 23.1, page 855): Nucleophilic carbonyl: aldehydes, ketones, esters, amides and nitrile
Chapter, Additions, Reactions, Chapter 32, Ketone, Condensation, Aldehydes, Carbonyl, Carbonyl condensation reactions
Download Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
Information
Domain:
Source:
Link to this page:
Please notify us if you found a problem with this document:
Documents from same domain
Overview of Korea’s Rapid Industrial - Vanderbilt University
as.vanderbilt.eduMiracle on the Han River Tae-Shin KWON President & CEO, Korea Economic Research Institute Miracle on the Han River and Beyond Overview of Korea’s Rapid Industrial Development and the Future President & CEO Tae-shin Kwon Korea Economic Research Institute Vanderbilt University, September 22nd, 2016.
Industrial, Overview, Korea, Miracle, Rapid, Overview of korea s rapid industrial
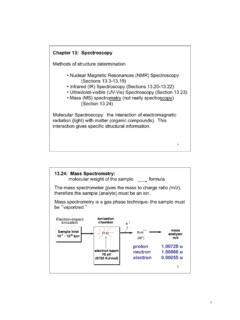
13.24: Mass Spectrometry - Vanderbilt University
as.vanderbilt.edu13.2: Principles of Molecular Spectroscopy: Quantized Energy Levels molecules have discrete energy levels (no continuum between levels) A molecule absorbs electromagnetic radiation when the energy of photon corresponds to the difference in ... 13.23 Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy
Massacre, Mardi Gras, and Torture in Early New Orleans
as.vanderbilt.eduMassacre, Mardi Gras, and Torture in Early New Orleans Sophie White T HE earliest known account of a Mardi Gras masquerade in New Orleans was produced by Marc-Antoine Caillot, a clerk for the
Orleans, Early, Massacre, Gras, Torture, Imrad, Mardi gras, And torture in early new orleans
Toward a Foucaultian Epistemology of Resistance: Counter ...
as.vanderbilt.eduFoucault calls subjugated knowledges3 are forms of experiencing and remembering that are pushed to the margins and rendered unqualified and unworthy of epistemic respect by …
Resistance, Foucault, Epistemology, A foucaultian epistemology of resistance, Foucaultian
Understanding Effort Reporting - College of Arts and Science
as.vanderbilt.eduVANDERBILT UNIVERSITY UNDERSTANDING EFFORT REPORTING INTRODUCTION This document has been developed to assist faculty and administrators in understanding the federal government's requirements for effort reporting.
Requirements, Understanding, Reporting, Efforts, Understanding effort reporting
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols - Vanderbilt University
as.vanderbilt.edu41 80 17.2: Properties of alcohols and phenols: Hydrogen bonding: The structure around the oxygen atom of an alcohol or phenol is similar to that in water and is sp3 hybridized Alcohols and phenols have much higher boiling points than
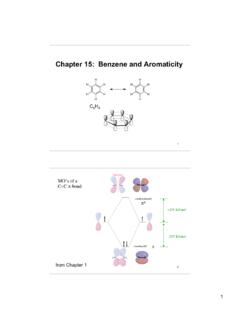
Chapter 15: Benzene and Aromaticity
as.vanderbilt.edu6 11 15.3: Structure and Stability of Benzene Formula: C 6H 6, four degrees of unsaturation (section 6.2) three double bonds + one ring The π-bonds of benzene are resistant to the normal reactions
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols
as.vanderbilt.edu17.7 Some reactions of alcohols A. Reactions involving the C-O bond Dehydration to alkenes: E1 mechanism (reactivity: 3° > 2° >> 1°) requires strong acid catalyst (H 2SO 4) water is a much better leaving group than HO-usually follows Zaitzev’s rule OH H 3CCCH 2CH 3 CH 3 H 2SO 4 H 2O, 3THF C H 3C H 3C C CH H H2C C H 23-H 2O 95 Dehydration ...
Ballet Folklórico- An Introduction
as.vanderbilt.eduBallet Folklórico- An Introduction Folkloric dance, like the English term “folk dance”, means dances of the people. This type of dance reflects the traditions, cultures and beliefs of people in a particular region.
The Legend of Popocatepetl & Iztaccíhuatl: A Love Story
as.vanderbilt.eduvolcanoes, including the massive Popocatepetl (Aztec for “smoking mountain.”) This detailed, oblique astronaut photograph also depicts a neighboring volcano, Iztaccíhuatl (the “Woman in White.”) With North to the right in the scene, the view is a westward-looking perspective.
Related documents
Reactions of Amines
web.mnstate.eduFrom Aldehydes or Ketones: Reductive Amination (Section 19-19) R R 1 O Ketone or aldehyde + H N R 3 R 2 NaBH 3C cat.H+ R R H 1 N 2R via N • Access: 1º, 2º, or 3º Amines • Mechanism: Not required. (Basic workup) • The carbonyl reactant can be an aldehyde or a ketone • The amine reactant must have at least one hydrogen, as shown above ...
Organometallic Chemistry - uni-regensburg.de
www-oc.chemie.uni-regensburg.deketones, alkyl halides, and esters. – Relative reactivity: RCOCl > RCHO > tosylates, iodides > epoxides > bromides >> ketones > esters > nitriles. • In reactions with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, the organocopper reagents prefer 1,4-addition …
Chemistry, Additions, Reactions, Ketone, Carbonyl, Organometallic chemistry, Organometallic
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols
as.vanderbilt.edu17.5: Alcohols from reduction of carbonyl compounds add the equivalent of H 2 across the π-bond of the carbonyl to give an alcohol RR' C O[H] R' RH H aldehyde (R or R´= H) → 1° alcohol ketone (R and R´≠ H) → 2° alcohol [H]: sodium borohydride: NaBH 4, ethanol reduces aldehydes to 1° alcohols and ketones to 2° alcohols
Transition Metal Carbonyls
alpha.chem.umb.educarbonyl product, which is greater for a low-valentmetal. Note that the first step in the case of an aldehydeis oxidative addition of the aldehydeC−H bond. It is much more difficult for the metal to break into a C−C bond so ketones, R 2CO, are usually resistant to this reaction.
NCERT
ncert.nic.inBoth aldehydes and ketones contain carbonyl group (>C = O) and are commonly known as carbonyl compounds. Identification of aldehydes and ketones is done by two important reactions of carbonyl group i.e. (i) addition reaction on double bond of >C = O group and (ii) oxidation of carbonyl group. Addition reactions of derivatives of ammonia are ...
Additions, Reactions, Ketone, Aldehydes and ketones, Aldehydes, Carbonyl, Of aldehydes and ketones, Addition reactions
12.112.112.1 Nomenclature and Structure of Carbonyl Group
ncert.nic.in361 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids The carbonyl carbon atom is sp2-hybridised and forms three sigma (σ) bonds. The fourth valence electron of carbon remains in its p-orbital and forms a π-bond with oxygen by overlap with p-orbital of an oxygen. In addition, the oxygen atom also has two non bonding electron pairs.
Carbonyl Chemistry (12 Lectures)
www.ch.ic.ac.ukCarbonyl Group Reactions ¥Addition Reactions ÐCarbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones undergo addition reactions. ÐThis is one of the most important reactions of the carbonyl group. O C + O C E E Y Y ¥Addition reactions occur by two different mechanisms: ÐBase-catalyzed addition (under basic or neutral conditions)
Lecture, Chemistry, Additions, Reactions, Ketone, Aldehydes and ketones, Aldehydes, Carbonyl, Carbonyl chemistry, Lecture 12, Addition reactions
CARBANIONS - SIUE
www.siue.eduaddition at the carbonyl group of another molecule. This process is a very important synthetic procedure and is known as the Aldol Condensation. The final product from aliphatic aldehydes or ketones contains both a carbonyl and an alcohol group. The product is called an aldol. CH 3CH=O CH 2CH=O CH 2=CH-O OH CH 3CH=O CH 2CH=O CH 3CH-O CH 2CH=O H ...