Transcription of NiCD/NiMH Fast-Charge Management IC datasheet …
1 1 Features Fast charge of nickel cadmiumor nickel-metal hydride batter-ies Direct LED output displayscharge status Fast-Charge termination by - V,maximum voltage, maximumtemperature, and maximumtime Internal band-gap voltage ref-erence Selectable pulse-trickle chargerates Low-power mode 8-pin 300-mil DIP or 150-milSOICG eneral DescriptionThe bq2002C Fast-Charge IC is a low-cost CMOS battery-chargecontrollerproviding reliable charge terminationfor both NiCd and NiMH battery appli-cations. Controlling a current-limitedor constant-current supply allows thebq2002C to be the basis for a cost-effective stand-alone or system-inte-grated charger.
2 The bq2002C inte-grates fast charge with pulsed-tricklecontrol in a single IC for charging oneor more NiCd orNiMH battery charge is initiated on applicationof the charging supply or batteryreplacement. For safety, fast charge isinhibited if the battery temperatureand voltage are outside charge is terminated by any ofthe following:nPeak voltage detection (PVD)nNegative delta voltage (- V)nMaximum voltagenMaximum temperaturenMaximum timeAfter fast charge, the bq2002C pulse-trickles the battery per the pre-configured limits. Fast charge may beinhibited using the INH pin. Thebq2002C may also be placed in low-standby-power mode to reducesystem power Fast-Charge Management ICbq2002 CTMT imer mode select inputLEDC harging status outputBATB attery voltage inputVSSS ystem DIP orNarrow SOIC234 8765 TMLEDBATVSSCCINHVCCTSTST emperature sense inputVCCS upply voltage inputINHC harge inhibit inputCCCharge control outputPin ConnectionsPin NamesSLUS136 - AUGUST 2011 Pin DescriptionsTMTimer mode inputA three-level input that controls the settingsfor the fast charge safety timer, voltage ter-mination mode, pulse-trickle.
3 And voltagehold-off output statusOpen-drain output that indicates the input voltageThe battery voltage sense input. The input tothis pin is created by a high-impedance re-sistor divider network connected betweenthe positive and negative terminals of groundTSTemperature sense inputInput for an external battery temperaturemonitoring voltage 20% power inhibit inputWhen high, INH suspends the fast charge inprogress. When returned low, the IC re-sumes operation at the point where control outputAn open-drain output used to control thecharging current to the battery. CC switch-ing to high impedance (Z) enables chargingcurrent to flow, and low to inhibit chargingcurrent.
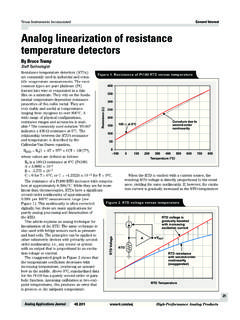
4 CC is modulated to provide DescriptionFigure 2 shows a state diagram and Figure 3 shows ablock diagram of the Voltage and TemperatureMeasurementsBattery voltage and temperature are monitored formaximum allowable values. The voltage presented onthe battery sense input, BAT, should represent asingle-cell potential for the battery under charge. Aresistor-divider ratio ofRB1RB2= N - 1is recommended to maintain the battery voltage withinthe valid range, where N is the number of cells, RB1 isthe resistor connected to the positive battery terminal,and RB2 is the resistor connected to the negativebattery terminal. See Figure :This resistor-divider network input impedance toend-to-end should be at least 200k and less than 1 M.
5 A ground-referenced negative temperature coefficientthermistor placed near the battery may be used as a low-cost temperature-to-voltage transducer. The temperaturesense voltage input at TS is developed using a resistor-thermistor network between VCCand VSS. See Figure +TSVSSBAT pin connectionThermistor connectionTMNTC = negative temperature coefficient for TMFigure 1. Voltage and Temperature Monitoring and TM Pin Configuration3bq2002 CChip onVCC Voltagetoo High?Battery Temperature?ChargePendingFastLED = Voltagetoo Low?VBAT < 2 VVTS < VCC/2 VTS > VCC/2 VBAT > andVBAT < 2V andVTS > VCC/2 VBAT < < VBAT VBAT > 2 VTrickleLED =FlashTrickleLED = ZVBAT > 2V orVTS < VCC/2 orPVD or - V or Maximum Time OutVBAT > 2 VVBAT 2 VFigure 2.
6 State DiagramOSCTMCCLEDVCCVSSBATINHC lockPhaseGeneratorTimingControlSampleHis toryA to Machine PVD, - V ALUF igure 3. Block DiagramStarting A Charge CycleEither of two events starts a charge cycle (see Figure 4):1. Application of power to VCCor2. Voltage at the BAT pin falling through the maximumcell voltage VMCV whereVMCV= 2V 5%.If the battery is within the configured temperature andvoltage limits, the IC begins fast charge. The validbattery voltage range is VLBAT<VBAT<VMCV,whereVLBAT= VCC 20%The valid temperature range is VTS>VHTF whereVHTF= VCC 5%.If VBAT VLBATor VTS VHTF, the IC enters the charge-pending state. In this state pulse trickle charge isapplied to the battery and the LED flashes until thevoltage and temperature come into the allowed fastcharge range or VBAT rises above VMCV.
7 Anytime VBAT VMCV, the IC enters the Charge Complete/BatteryAbsent state. In this state the LED is off and tricklecharge is applied to the battery until the next newcharge cycle charge continues until termination by one or more ofthe five possible termination conditions:nPeak voltage detection (PVD)nNegative delta voltage (- V)nMaximum voltagenMaximum temperaturenMaximum time4 CorrespondingFast-ChargeRateTMTerminatio nTypicalFast-ChargeTime Limits(minutes)Typical PVDand - VHold-OffTime (seconds)Pulse-TrickleRatePulse-TrickleP ulse Width(ms)MaximumSynchronizedSamplingPeri od(seconds)C/2 MidPVD160300 V4075 :Typical conditions = 25 C, VCC= = *VCC on all timing is 12%.
8 Table 1. Fast-Charge Safety Time/Hold-Off ChargingVCC = 0 Fast ChargingCC OutputLEDC harge initiated by application of power Charge initiated by battery replacement Pulse-TrickleSeeTable 11sFigure 4. Charge Cycle Phases_____PVD and - V Termination There are two modes for voltage termination, depending on the state of TM. For - V (TM = high), if V BAT is lower than any previously measured value by 12mV 3mV, fast charge is terminated. For PVD (TM = low or mid), a decrease of terminates fast charge. The PVD and - V tests are valid in the range 1V<VBAT <2V. Synchronized Voltage Sampling Voltage sampling at the BAT pin for PVD and - V termi nation may be synchronized to an external stimulus using the INH input.
9 Low-high-low input pulses between 100ns and in width must be applied at the INH pin with a frequency greater than the maximum synchronized sampling period set by the state of the TM pin as shown in Table 1. Voltage is sampled on the falling edge of such pulses. If the time between pulses is greater than the synchronizing period, voltage sampling free-runs at once every 17 seconds. A sample is taken by averaging together voltage measurements taken 57 s apart. The IC takes 32 measurements in PVD mode and 16 measurements in - V mode. The resulting sample periods ( and , respectively) filter out harmonics centered around 55 and 109Hz.
10 This technique minimizes the effect of any AC line ripple that may feed through the power supply from either 50 or 60Hz AC sources. If the INH input remains high for more than 12ms, the voltage sample history kept by the IC and used for PVD and - V termination decisions is erased and a new history is started. Such a reset is required when transitioning from free-running to synchronized voltage sampling. The response of the IC to pulses less than 100ns in width or between and 12ms is indeterminate. The tolerance on all timing is 12%. Voltage Termination Hold-off A hold-off period occurs at the start of fast charging. During the hold-off time, the PVD and - V terminations are disabled.