Transcription of Switching loss Switch applications - UIC Engineering
1 fundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realization Switch RealizationSwitch applicationsSingle-, two-, and four-quadrant switches. Synchronous rectifiersA brief survey of power semiconductor devicesPower diodes, MOSFETs, BJTs, IGBTs, and thyristorsSwitching lossTransistor Switching with clamped inductive load. Diode recovered charge. Stray capacitances and inductances, and ringing. Efficiency vs. Switching of power Electronics Switch realizationSPST (single-pole single-throw) switchesiv+ 10 SPST Switch , with voltage and current polarities definedLCR+V iL(t)+ Vg12 Buck converterLCR+V iL(t)+ Vg+ vA vB+ABiAiBwith SPDT Switch :with two SPST switches:All power semiconductor devices function as SPST of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationRealization of SPDT Switch using two SPST switcheslA nontrivial step: two SPST switches are not exactly equivalent to one SPDT switchlIt is possible for both SPST switches to be simultaneously ON or OFFlBehavior of converter is then significantly modified discontinuous conduction modes (ch.)
2 5)lConducting state of SPST Switch may depend on applied voltage or current for example: diodeFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationQuadrants of SPST Switch operationiv+ 10switchoff-state voltageswitchon-statecurrentA single-quadrant Switch example:ON-state: i > 0 OFF-state: v > 0 fundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationSome basic Switch applicationsswitchoff-state voltageswitchon-statecurrentswitchon-sta tecurrentswitchoff-statevoltageswitchon- statecurrentswitchoff-statevoltageswitch on-statecurrentswitchoff-statevoltageSin gle-quadrant switchCurrent-bidirectional two-quadrant switchVoltage-bidirectional two-quadrant switchFour-quadrant switchFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch Single-quadrant switchesiv+ 10 Active Switch : Switch state is controlled exclusively by a third terminal (control terminal).
3 Passive Switch : Switch state is controlled by the applied current and/or voltage at terminals 1 and : A special case turn-on transition is active, while turn-off transition is Switch : on-state i(t) and off-state v(t) are of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationThe diodei10v+ ivonoffSymbolinstantaneous i-v characteristic A passive Switch Single-quadrant Switch : can conduct positive on-state current can block negative off-state voltage provided that the intended on-state and off-state operating points lie on the diode i-v characteristic, then Switch can be realized using a diodeFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationThe Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) and the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)i10v+ Ci10v+ CBJTIGBT ivonoffinstantaneous i-v characteristic An active Switch , controlled by terminal C Single-quadrant Switch .
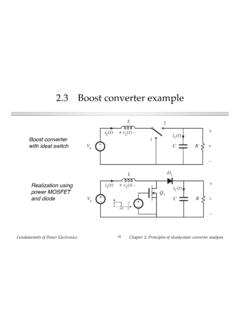
4 Can conduct positive on-state current can block positive off-state voltage provided that the intended on-state and off-state operating points lie on the transistor i-v characteristic, then Switch can be realized using a BJT or IGBTF undamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationThe Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)i10v+ Civonoffon(reverse conduction)Symbolinstantaneous i-v characteristic An active Switch , controlled by terminal C Normally operated as single-quadrant Switch : can conduct positive on-state current (can also conduct negative current in some circumstances) can block positive off-state voltage provided that the intended on-state and off-state operating points lie on the MOSFET i-v characteristic, then Switch can be realized using a MOSFETF undamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationRealization of Switch using transistors and diodesLCR+V iL(t)+ Vg+ vA vB+ABiAiBBuck converter exampleiAvAiLVgswitch Aonswitch AoffiBvBiL Vgswitch Bonswitch BoffSPST Switch operating pointsSwitch ASwitch BSwitch A: transistorSwitch B.
5 DiodeFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationRealization of buck converterusing single-quadrant switches+ VgLiL(t)iAvAvB+ iBvL(t)+ + iAvAiLVgswitch Aonswitch AoffiBvBiL Vgswitch Bonswitch BoffFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationCurrent-bidirectionaltwo-quad rant switchesi10v+ Civon(transistor conducts)offon(diode conducts)BJT / anti-parallel diode realizationinstantaneous i-v characteristic Usually an active Switch , controlled by terminal C Normally operated as two-quadrant Switch : can conduct positive or negative on-state current can block positive off-state voltage provided that the intended on-state and off-state operating points lie on the composite i-v characteristic, then Switch can be realized as shownFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationTwo quadrant switchesswitchon-statecurrentswitchoff-s tatevoltageivon(transistor conducts)offon(diode conducts)iv+ 10 fundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationMOSFET body diodei10v+ Civon(transistor conducts)offon(diode conducts) power MOSFET, and its integral body diodeUse of external diodes to prevent conduction of body diodePower MOSFET characteristicsFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationA simple inverter+ L+ VgVgCRQ1Q2D1D2iLiAiBv0+ vB+ vA+ v0(t)
6 =(2D 1)VgFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationInverter: sinusoidal modulation of Dv0(t)=(2D 1)VgD(t) = +Dmsin ( t)v0 DVg modulation to produce ac output:iL(t)=v0(t)R=(2D 1)VgRThe resulting inductor current variation is also sinusoidal:Hence, current-bidirectional two-quadrant switches are of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationThe dc-3 ac voltage source inverter (VSI)+ VgiaibicSwitches must block dc input voltage, and conduct ac load of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationBidirectional battery charger/dischargerLQ1Q2D1D2vbatt+ vbusspacecraftmain power bus+ vbus > vbattA dc-dc converter with bidirectional power of power ElectronicsSwitch Voltage-bidirectional two-quadrant switchesBJT / series diode realizationinstantaneous i-v characteristic Usually an active Switch , controlled by terminal C Normally operated as two-quadrant Switch .
7 Can conduct positive on-state current can block positive or negative off-state voltage provided that the intended on-state and off-state operating points lie on the composite i-v characteristic, then Switch can be realized as shown The SCR is such a device, without controlled turn-offi10v+ Civonoff(transistorblocks voltage)off(diodeblocks voltage) fundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationTwo-quadrant switchesiv+ 10ivonoff(transistorblocks voltage)off(diodeblocks voltage)switchon-statecurrentswitchoff-s tatevoltagei10v+ CFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationA dc-3 ac buck-boost inverter+ iLVg a b c+vab(t) +vbc(t) Requires voltage-bidirectional two-quadrant example: boost-type inverter, or current-source inverter (CSI). fundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realization Four-quadrant switchesswitchon-statecurrentswitchoff-s tatevoltage Usually an active Switch , controlled by terminal C can conduct positive or negative on-state current can block positive or negative off-state voltageFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationThree ways to realize a four-quadrant switchi10v+ i10v+ i10v+ iv+ 10 fundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationA 3 ac-3 ac matrix converteribicia+ + + van(t)vcn(t)vbn(t)3 ac input3 ac output All voltages and currents are ac; hence, four-quadrant switches are required.
8 Requires nine four-quadrant switchesFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realization Synchronous rectifiersiv+ 10i10v+ Civonoffon(reverse conduction)Replacement of diode with a backwards-connected MOSFET,to obtain reduced conduction lossi10v+ ideal switchconventional diode rectifierMOSFET as synchronous rectifierinstantaneous i-v characteristicFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationBuck converter with synchronous rectifier+ VgLiL(t)iAvAvB+ iB+ Q1Q2CC MOSFET Q2 is controlled to turn on when diode would normally conduct Semiconductor conduction loss can be made arbitrarily small, by reduction of MOSFET on-resistances Useful in low-voltage high-current applicationsFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationPower diodesA power diode, under reverse-biased conditions.
9 Low doping concentration{{pn-n+ depletion region, reverse-biased+++ v v +EFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationForward-biased power diodeconductivity modulationpn-n+ minority carrier injection+++ +++iv{ fundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationTypical diode Switching waveformsti(t)area Qr0v(t)tr(1)(2)(3)(4)(5)(6)tdidtFundamen tals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationThe power MOSFETD rainnn-nnppSourceGatenn Gate lengths approaching one micron Consists of many small enhancement-mode parallel-connected MOSFET cells, covering the surface of the silicon wafer Vertical current flow n-channel device is shownFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationMOSFET: Off statenn-nnppnndepletion region +sourcedrain p-n- junction is reverse-biased off-state voltage appears across n- regionFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationMOSFET.}}}
10 On statenn-nnppnnchannelsourcedraindrain current p-n- junction is slightly reverse-biased positive gate voltage induces conducting channel drain current flows through n- region and conducting channel on resistance = total resistances of n- region, conducting channel, source and drain contacts, of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationMOSFET body diodenn-nnppnnBody diodesourcedrain p-n- junction forms an effective diode, in parallel with the channel negative drain-to-source voltage can forward-bias the body diode diode can conduct the full MOSFET rated current diode Switching speed not optimized body diode is slow, Qr is largeFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationTypical MOSFET characteristics0A5A10 AVGSIDVDS = = 1 VVDS = 2 VVDS = 10 VVDS = 200V0V5V10V15 Voffstateon state Off state: VGS < Vth On state: VGS >> Vth MOSFET can conduct peak currents well in excess of average current rating characteristics are unchanged on-resistance has positive temperature coefficient, hence easy to parallelFundamentals of power ElectronicsSwitch realizationA simple MOSFET equivalent circuitDSGCdsCgsCgd Cgs : large, essentially constant Cgd : small, highly nonlinear Cds.